Volume 12, Issue 4 (2024)
Health Educ Health Promot 2024, 12(4): 617-622 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Ruwayda R, Hastono S, Siregar K, Martha E, Nurdini L. Village Midwife Performance in Maternal and Child Health Services in Jambi Province, Indonesia. Health Educ Health Promot 2024; 12 (4) :617-622
URL: http://hehp.modares.ac.ir/article-5-77876-en.html
URL: http://hehp.modares.ac.ir/article-5-77876-en.html
1- Department of Public Health, Faculty of Public Health, University of Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Attitude [MeSH], Community Health Workers [MeSH], Midwifery [MeSH], Training Support [MeSH], Maternal Death [MeSH], Child Health [MeSH]
Full-Text [PDF 610 kb]
(1471 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (782 Views)
Full-Text: (61 Views)
Introduction
The goal of the maternal health care quality assurance system is to reduce the maternal mortality ratio (MMR) to fewer than 70 per 100,000 live births in order to attain Universal Health Coverage (UHC) by 2030. In Tanzania, among the 556 maternal deaths, 71.8% were attributed to a lack of knowledge and skills among health workers [1]. Numerous studies have shown that high-quality care can prevent two-thirds of maternal and newborn deaths, potentially saving 4.3 million lives annually [2, 3].
In 2020, low- and lower-middle-income nations accounted for about 95% of all maternal deaths, the majority of which were avoidable. Regions and sub-regions of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are used here. Approximately 87% (253000) of the anticipated global maternal fatalities in 2020 occurred in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia. The two regions with the largest overall reductions in maternal mortality ratios (MMRs) between 2000 and 2020 were Eastern Europe (from an MMR of 38 to 11) and Southern Asia (from an MMR of 408 to 134). Even though its MMR in 2020 was quite high, Sub-Saharan Africa also saw a significant 33% decrease in MMR between 2000 and 2020. Over this time, the MMRs of four SDG sub-regions were approximately halved: The MMR decreased by almost one-third in Eastern Africa, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, Northern Africa, and Western Europe [4].
In Indonesia, the maternal mortality rate is 305 per 100,000 births, primarily caused by eclampsia, bleeding, and infections, with 78% of these deaths occurring in healthcare facilities. The predetermined target is to reduce this rate to 183 per 100,000 births by 2024, and the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim for a reduction to 70 per 100,000 live births. Comparing current achievements to these targets, it is evident that the program's realization requires targeted interventions and policy adjustments to enhance health human resources [5]. Determinants of maternal mortality include direct causes such as obstetric complications like bleeding, eclampsia, and infection. Intermediate causes encompass reproductive health status, access to healthcare, and health-related behaviors. Indirect causes involve factors like education and employment status [6]. Midwives play a critical role in addressing public health challenges, requiring them to possess the competence to deliver safe, high-quality, and efficient health services throughout their lifespan [7].
A qualitative study in Nigeria demonstrated efforts to reduce maternal mortality by integrating midwives as community-based providers within the healthcare system. This integration aimed to enhance the quality of maternal and newborn care through active community involvement [8]. A study in Bangladesh identified a women-centered midwifery model of care that enhances continuity of care. However, challenges include limited community accessibility, insufficient prioritization of care standards, and inadequate community involvement and integration of healthcare systems to fully promote the benefits of midwifery care [9]. The demand for midwifery competence is expected to enhance the quality of maternal health services in the community. Studies in Pakistan have shown that community midwife programs can improve women’s access to safe pregnancy and delivery services through effective communication and outreach [10]. Another study in India found that midwives played a key role in shifting the perspectives and cultural attitudes of remote communities regarding effective healthcare systems [11-15].
This study is considered important because it provides in-depth insights into the factors affecting the performance of village midwives. By understanding these determinants, policies and programs can be designed to enhance the capacity of midwives in delivering maternal and child health services. This could lower death rates and enhance general health by raising the standard of care given to expectant mothers and their unborn children. The findings of this study can serve as a basis for creating health policies that are more successful. The data obtained allows policymakers to identify areas that require special attention, whether in terms of training, resources, or infrastructure support. This will aid in the more efficient and targeted allocation of resources.
This research has aimed to analyze determinants of village midwife performance in maternal and child health services in Jambi Province, Indonesia.
Instrument and Methods
This cross-sectional descriptive study was carried out in Indonesia's Jambi Province's Muaro Jambi District. This research has been carried out for two months starting from February to March 2024. The sample size was calculated using the OpenEpi sample size calculator, based on a 7.5% performance prevalence of village midwives [16], a total population of 333, a 95% confidence level, and a 5% margin of error. The estimated sample size was 180. However, 9 samples were removed due to a considerable amount of missing information. Therefore, a total of 171 village midwives from Muaro Jambi District, Jambi Province, participated in the study. Inclusion criteria required participants to be village midwives with more than two years of experience. Exclusion criteria included retired midwives and those unwilling to participate. Participants were selected based on data from the Muaro Jambi District Health Office and village mapping. In villages with two midwives, one was chosen according to the inclusion criteria.
The study utilized a performance instrument for village midwives in the Maternal and Child Health program provided by the Indonesian Ministry of Health. The questionnaire on the performance of village midwives was adapted from the research by Yunita et al. and consisted of 10 questions [16]. Responses were scored as either 1 for 'completed' or 0 for 'not completed'. The performance of the village midwives was categorized into two objective criteria; Good (if the respondent's score was equal to 6) and poor (if the score was less than 6). The questionnaire was validated, as all question items were deemed valid with a calculated r-value greater than 0.3. Reliability was also confirmed, with a Cronbach's alpha value exceeding 0.6, indicating high consistency. For assessing supervision, training, and attitudes, questionnaires were adapted from previous research. The supervision parameter was assessed using a questionnaire consisting of 5 indicator questions. Two objective criteria were used to evaluate supervision; 'ever' (if the respondent's score was equal to 4) and 'never' (if the score was less than 4). The training parameter was measured using a similar 5-question questionnaire, applying a Guttman scale with scores of 0 and 1. The same criteria ('ever' (score=4) and 'never' (score<4)) were applied to the training parameter. For the attitude parameter, a 7-question questionnaire was used, also employing a Guttman scale with scores of 0 and 1. Attitudes were classified as either 'positive' (if the respondent's score was equal to 5) or 'negative' (if the score was less than 5).
This study was conducted in February-March 2024 at Muaro Jambi Regency, Jambi Province and 2 Staff of Muaro Jambi district health office, trained previously using the instrument were enlisted. Before all respondents received a thorough explanation of the goals and procedures involved in data collection.
SPSS 20.0 was used for data entry and analysis. Frequency and percentages were calculated for categorical parameters including age, education level, marital status, length of service, use of official vehicles, training, rewards, supervision, and attitudes. Inferential statistics were investigated using the Chi-square test to determine the relationship between village midwifery and its general features. Statistical significance was defined as a p-value of less than 0.05. Additionally, binary logistic regression was used to find possible parameters that could affect village midwifery performance.
Prior to data collection, all participants signed an informed consent form, and the research ethics committee of Universitas Jambi, Indonesia, granted permission to perform this study (Number: 572/UN21.8/PT.01.04/2024).
Findings
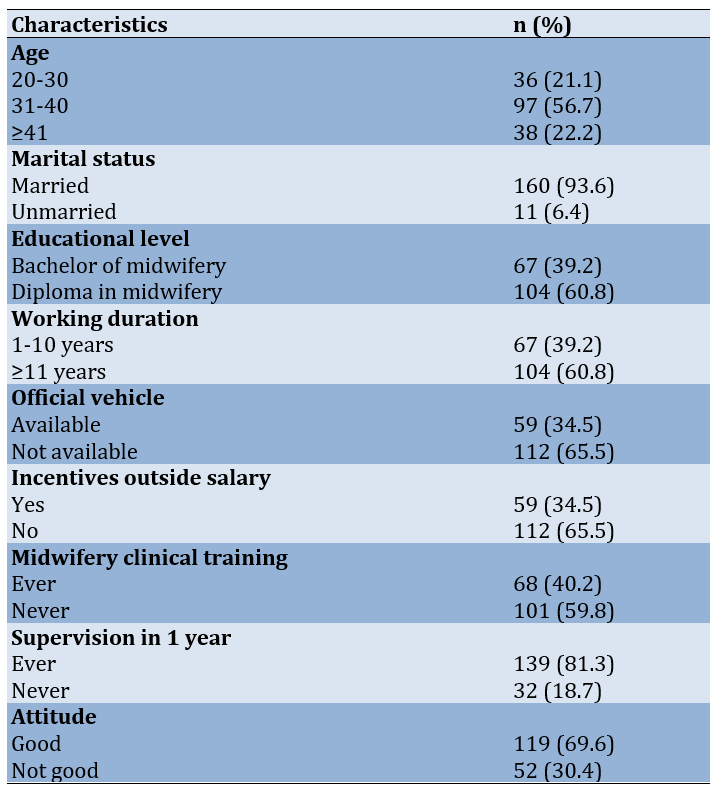
The majority of midwives who participated in the study were aged 31-40 years (97 midwives, 56.7%), married (160 midwives, 93.6%), and held a Diploma 3 in midwifery (104 midwives, 60.8%). Most had been working for 11 years or more (104 midwives, 60.8%), did not use government vehicles (112 midwives, 65.5%), and did not receive compensation (112 midwives, 65.5%). Additionally, 101 midwives (59.8%) had never attended training, while 139 (81.3%) had received training, and 119 midwives (69.9%) exhibited a predominantly positive attitude (Table 1).
Table 1. Demographic characteristics of the participants
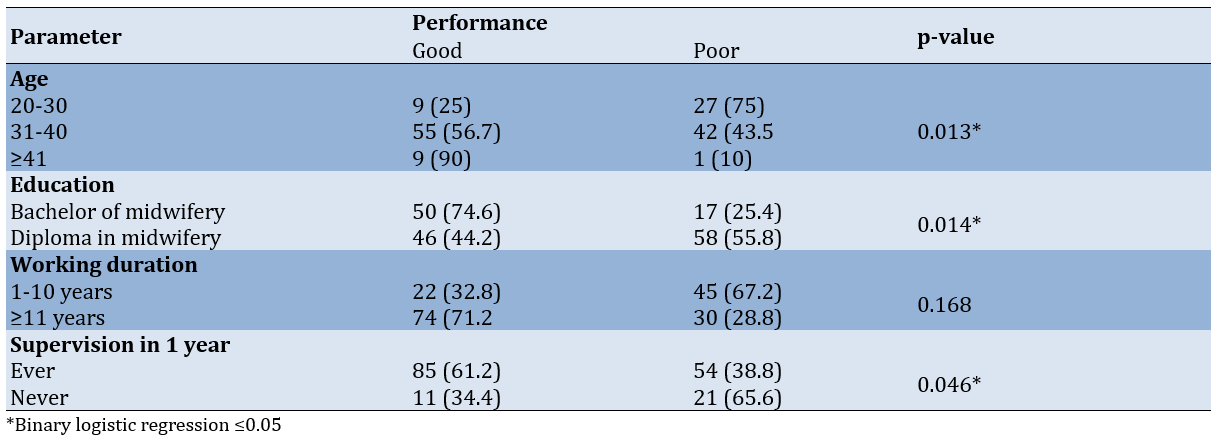
The statistically significant parameters were age, education, length of employment, and supervision within the past year (Table 2).
Table 2. Factors associated with the performance of village midwives in MCH services
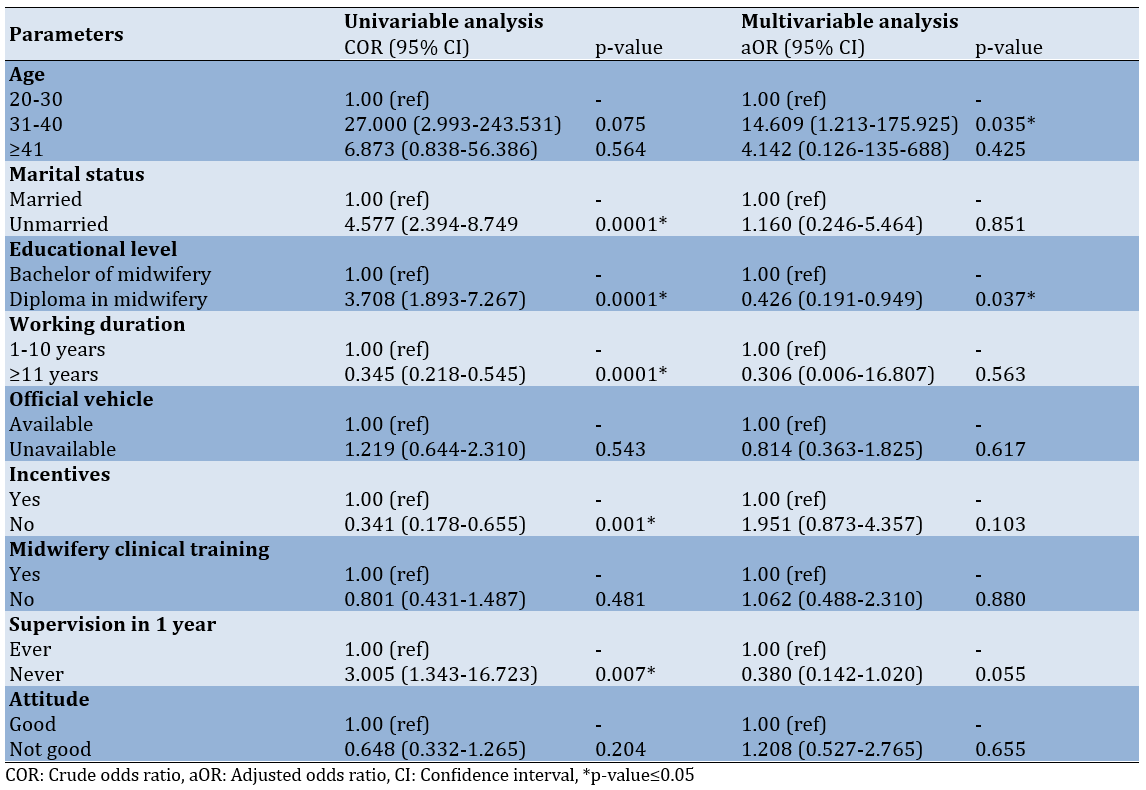
According to the logistic regression analysis, significant parameters in the univariate analysis include age, education level, length of service, incentives outside salary, and supervision within the past year. In the multivariate analysis, the significant parameters were age and education level (Table 3).
Table 3. Binary logistic regression analysis for predicting the performance of village midwives
Discussion
This research has aimed to analyze determinants of village midwife performance in maternal and child health services in Jambi Province, Indonesia. There was no observed relationship between supervision and the performance improvement of village midwives. Various factors contributed to midwife performance. Research conducted at Puskesmas Pidie, Aceh, reveals that organizational factors significantly impact midwife performance, particularly compensation. Midwives who receive adequate compensation tend to perform better than those with insufficient compensation. Factors such as experience, demographics, motivation, satisfaction, and compensation levels greatly influence performance. Specifically, poor performance is likely in 99.8% of cases where experience, demographics, motivation, satisfaction, and compensation are lacking. Conversely, when midwives benefit from substantial experience, favorable demographics, strong motivation, high satisfaction, and good compensation, the likelihood of achieving good performance increases to 4.8% [17].
The majority of village midwives had not participated in midwifery clinical training. Despite evidence indicating that such training can enhance midwives' performance by improving their knowledge and practical skills to meet established standards, many had yet to benefit from it. To achieve meaningful improvements in midwifery practice, it is essential to provide ongoing training, strengthen capacity, and secure robust community support [18]. Research has conducted by the Australia Indonesia Partnership for Maternal and Neonatal Health (AIPMNH) in Nusa Tenggara Timur have revealed a low level of knowledge and skills among coordinator midwives (Bikor) prior to training. Notably, their skill levels do not significantly differ from those of junior midwives even 2-3 years post-training. Factors such as education and recent childbirth experience are found to influence the skill levels of Bikor. To address these gaps, it is crucial to enhance skills through Clinical Instruction (CI) training and regular clinical practice. While consistent practice can lead to skill improvement over the first 6 months, it is important to note that skills may decline after 2 years without ongoing training and support [19].
Research conducted in Tanah Datar District identifies several parameters associated with midwife performance: Length of service, supervision by coordinating midwives, motivation, and job satisfaction [20]. The suboptimal performance of midwifery services in South Aceh Regency can be attributed to insufficient guidance from the Health Office, as well as low levels of knowledge and motivation among midwives [21]. Research in Bangli Regency demonstrates a significant relationship between the performance of village midwives and factors such as competence, financial compensation, and supervision. Among these parameters, supervision has the most substantial impact, influencing midwife performance 25 times more than the other factors. Adiputri et al.'s research [22] in Semarang reveals that facilitative supervision lacked formal preparation, consisting only of an assignment letter and a checklist. Both Bikor and PMB had not received specialized training or socialization related to facilitative supervision. Instead, Bikor was provided solely with a checklist by the Health Office as an assessment guideline, without a reference book for facilitative supervision. Additionally, orientation on the checklist for PMB was not conducted for all Bikors. Consequently, critical components of facilitative supervision, such as self-assessment by PMB and verification by Bikor in collaboration with PMB, were not implemented. As a result, follow-up supervision was solely based on Bikors' assessments. Supervision often took the form of unscheduled inspections without prior agreement on the implementation schedule with PMB, occurring during working hours at the Public Health Center.
To enhance the performance and professionalism of midwives, mentoring relationships are crucial for developing professional confidence. These relationships should be structured with clear duration and agreements. Mentors are responsible for listening, challenging, supporting, and guiding their mentees, fostering research, exploration, and reflective practice. While the mentored midwife retains responsibility for her practice and obligations, senior midwives or mentors play a key role in guiding less experienced colleagues to improve performance, service quality, and address areas of poor performance. Performance supervision can be conducted through supportive, statutory, and professional supervision methods [23].
Research conducted in Belgium examine the relationship between advanced midwifery practitioners' task performance and their competencies across various domains. The study found that certain tasks, such as research and clinical expertise, were performed inadequately. This underperformance was attributed to factors related to work organization, competency deficiencies, and insufficient leadership [24]. Research in Ethiopia express that autocratic leadership is the most common style among midwifery leaders and has a negative effect on midwives' performance. Democratic and laissez-faire leadership styles are associated with improved performance [25]. Research in Sudan indicates that supervision of midwives can significantly enhance service quality. It also aids in developing robust supervision systems, increases active engagement within the community, and strengthens the relationships between health facilities and midwives. Additionally, effective supervision can boost public trust in midwives [26-29].
Study limitation
The strict inclusion criteria may limit the generalizability of the study's findings. For instance, only midwives with more than two years of experience were included, potentially excluding insights into the performance of newer midwives or those with differing professional backgrounds. Additionally, participant selection based on Health Office data and village mapping could introduce bias if the data is incomplete or inaccurate, which may affect the overall representativeness of the sample.
Strength and recommendation
This research is highly relevant to the local context of Muaro Jambi, offering valuable insights for policy development and improved planning of public health programs in the region. The study also provides recommendations for fostering partnerships between the government, educational institutions, and health organizations to support training and professional development initiatives for village midwives.
Conclusion
Age and education level are key determinants of village midwives' performance in maternal and child health services.
Acknowledgments: The authors would like to thank all participants for their participation and cooperation throughout the study. They also thank the Faculty of Public Health of the University of Indonesia and the Health Polytechnic of the Jambi Ministry of Health for their support and assistance.
Ethical Permissions: Prior to data collection, all participants signed an informed consent form, and the research ethics committee of Universitas Jambi, Indonesia, granted permission to perform this study (Number: 572/UN21.8/PT.01.04/2024).
Conflicts of Interests: None declared.
Authors' Contribution: Ruwayda R (First Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Methodologist/Discussion Writer/Statistical Analyst (40%); Hastono SP (Second Author), Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (20%); Siregar KN (Third Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (20%); Martha E (Fourth Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (10%); Nurdini L (Fifth Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (10%)
Funding/Support: None Funding.
The goal of the maternal health care quality assurance system is to reduce the maternal mortality ratio (MMR) to fewer than 70 per 100,000 live births in order to attain Universal Health Coverage (UHC) by 2030. In Tanzania, among the 556 maternal deaths, 71.8% were attributed to a lack of knowledge and skills among health workers [1]. Numerous studies have shown that high-quality care can prevent two-thirds of maternal and newborn deaths, potentially saving 4.3 million lives annually [2, 3].
In 2020, low- and lower-middle-income nations accounted for about 95% of all maternal deaths, the majority of which were avoidable. Regions and sub-regions of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are used here. Approximately 87% (253000) of the anticipated global maternal fatalities in 2020 occurred in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia. The two regions with the largest overall reductions in maternal mortality ratios (MMRs) between 2000 and 2020 were Eastern Europe (from an MMR of 38 to 11) and Southern Asia (from an MMR of 408 to 134). Even though its MMR in 2020 was quite high, Sub-Saharan Africa also saw a significant 33% decrease in MMR between 2000 and 2020. Over this time, the MMRs of four SDG sub-regions were approximately halved: The MMR decreased by almost one-third in Eastern Africa, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, Northern Africa, and Western Europe [4].
In Indonesia, the maternal mortality rate is 305 per 100,000 births, primarily caused by eclampsia, bleeding, and infections, with 78% of these deaths occurring in healthcare facilities. The predetermined target is to reduce this rate to 183 per 100,000 births by 2024, and the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim for a reduction to 70 per 100,000 live births. Comparing current achievements to these targets, it is evident that the program's realization requires targeted interventions and policy adjustments to enhance health human resources [5]. Determinants of maternal mortality include direct causes such as obstetric complications like bleeding, eclampsia, and infection. Intermediate causes encompass reproductive health status, access to healthcare, and health-related behaviors. Indirect causes involve factors like education and employment status [6]. Midwives play a critical role in addressing public health challenges, requiring them to possess the competence to deliver safe, high-quality, and efficient health services throughout their lifespan [7].
A qualitative study in Nigeria demonstrated efforts to reduce maternal mortality by integrating midwives as community-based providers within the healthcare system. This integration aimed to enhance the quality of maternal and newborn care through active community involvement [8]. A study in Bangladesh identified a women-centered midwifery model of care that enhances continuity of care. However, challenges include limited community accessibility, insufficient prioritization of care standards, and inadequate community involvement and integration of healthcare systems to fully promote the benefits of midwifery care [9]. The demand for midwifery competence is expected to enhance the quality of maternal health services in the community. Studies in Pakistan have shown that community midwife programs can improve women’s access to safe pregnancy and delivery services through effective communication and outreach [10]. Another study in India found that midwives played a key role in shifting the perspectives and cultural attitudes of remote communities regarding effective healthcare systems [11-15].
This study is considered important because it provides in-depth insights into the factors affecting the performance of village midwives. By understanding these determinants, policies and programs can be designed to enhance the capacity of midwives in delivering maternal and child health services. This could lower death rates and enhance general health by raising the standard of care given to expectant mothers and their unborn children. The findings of this study can serve as a basis for creating health policies that are more successful. The data obtained allows policymakers to identify areas that require special attention, whether in terms of training, resources, or infrastructure support. This will aid in the more efficient and targeted allocation of resources.
This research has aimed to analyze determinants of village midwife performance in maternal and child health services in Jambi Province, Indonesia.
Instrument and Methods
This cross-sectional descriptive study was carried out in Indonesia's Jambi Province's Muaro Jambi District. This research has been carried out for two months starting from February to March 2024. The sample size was calculated using the OpenEpi sample size calculator, based on a 7.5% performance prevalence of village midwives [16], a total population of 333, a 95% confidence level, and a 5% margin of error. The estimated sample size was 180. However, 9 samples were removed due to a considerable amount of missing information. Therefore, a total of 171 village midwives from Muaro Jambi District, Jambi Province, participated in the study. Inclusion criteria required participants to be village midwives with more than two years of experience. Exclusion criteria included retired midwives and those unwilling to participate. Participants were selected based on data from the Muaro Jambi District Health Office and village mapping. In villages with two midwives, one was chosen according to the inclusion criteria.
The study utilized a performance instrument for village midwives in the Maternal and Child Health program provided by the Indonesian Ministry of Health. The questionnaire on the performance of village midwives was adapted from the research by Yunita et al. and consisted of 10 questions [16]. Responses were scored as either 1 for 'completed' or 0 for 'not completed'. The performance of the village midwives was categorized into two objective criteria; Good (if the respondent's score was equal to 6) and poor (if the score was less than 6). The questionnaire was validated, as all question items were deemed valid with a calculated r-value greater than 0.3. Reliability was also confirmed, with a Cronbach's alpha value exceeding 0.6, indicating high consistency. For assessing supervision, training, and attitudes, questionnaires were adapted from previous research. The supervision parameter was assessed using a questionnaire consisting of 5 indicator questions. Two objective criteria were used to evaluate supervision; 'ever' (if the respondent's score was equal to 4) and 'never' (if the score was less than 4). The training parameter was measured using a similar 5-question questionnaire, applying a Guttman scale with scores of 0 and 1. The same criteria ('ever' (score=4) and 'never' (score<4)) were applied to the training parameter. For the attitude parameter, a 7-question questionnaire was used, also employing a Guttman scale with scores of 0 and 1. Attitudes were classified as either 'positive' (if the respondent's score was equal to 5) or 'negative' (if the score was less than 5).
This study was conducted in February-March 2024 at Muaro Jambi Regency, Jambi Province and 2 Staff of Muaro Jambi district health office, trained previously using the instrument were enlisted. Before all respondents received a thorough explanation of the goals and procedures involved in data collection.
SPSS 20.0 was used for data entry and analysis. Frequency and percentages were calculated for categorical parameters including age, education level, marital status, length of service, use of official vehicles, training, rewards, supervision, and attitudes. Inferential statistics were investigated using the Chi-square test to determine the relationship between village midwifery and its general features. Statistical significance was defined as a p-value of less than 0.05. Additionally, binary logistic regression was used to find possible parameters that could affect village midwifery performance.
Prior to data collection, all participants signed an informed consent form, and the research ethics committee of Universitas Jambi, Indonesia, granted permission to perform this study (Number: 572/UN21.8/PT.01.04/2024).
Findings
The majority of midwives who participated in the study were aged 31-40 years (97 midwives, 56.7%), married (160 midwives, 93.6%), and held a Diploma 3 in midwifery (104 midwives, 60.8%). Most had been working for 11 years or more (104 midwives, 60.8%), did not use government vehicles (112 midwives, 65.5%), and did not receive compensation (112 midwives, 65.5%). Additionally, 101 midwives (59.8%) had never attended training, while 139 (81.3%) had received training, and 119 midwives (69.9%) exhibited a predominantly positive attitude (Table 1).
Table 1. Demographic characteristics of the participants

The statistically significant parameters were age, education, length of employment, and supervision within the past year (Table 2).
Table 2. Factors associated with the performance of village midwives in MCH services

According to the logistic regression analysis, significant parameters in the univariate analysis include age, education level, length of service, incentives outside salary, and supervision within the past year. In the multivariate analysis, the significant parameters were age and education level (Table 3).
Table 3. Binary logistic regression analysis for predicting the performance of village midwives

Discussion
This research has aimed to analyze determinants of village midwife performance in maternal and child health services in Jambi Province, Indonesia. There was no observed relationship between supervision and the performance improvement of village midwives. Various factors contributed to midwife performance. Research conducted at Puskesmas Pidie, Aceh, reveals that organizational factors significantly impact midwife performance, particularly compensation. Midwives who receive adequate compensation tend to perform better than those with insufficient compensation. Factors such as experience, demographics, motivation, satisfaction, and compensation levels greatly influence performance. Specifically, poor performance is likely in 99.8% of cases where experience, demographics, motivation, satisfaction, and compensation are lacking. Conversely, when midwives benefit from substantial experience, favorable demographics, strong motivation, high satisfaction, and good compensation, the likelihood of achieving good performance increases to 4.8% [17].
The majority of village midwives had not participated in midwifery clinical training. Despite evidence indicating that such training can enhance midwives' performance by improving their knowledge and practical skills to meet established standards, many had yet to benefit from it. To achieve meaningful improvements in midwifery practice, it is essential to provide ongoing training, strengthen capacity, and secure robust community support [18]. Research has conducted by the Australia Indonesia Partnership for Maternal and Neonatal Health (AIPMNH) in Nusa Tenggara Timur have revealed a low level of knowledge and skills among coordinator midwives (Bikor) prior to training. Notably, their skill levels do not significantly differ from those of junior midwives even 2-3 years post-training. Factors such as education and recent childbirth experience are found to influence the skill levels of Bikor. To address these gaps, it is crucial to enhance skills through Clinical Instruction (CI) training and regular clinical practice. While consistent practice can lead to skill improvement over the first 6 months, it is important to note that skills may decline after 2 years without ongoing training and support [19].
Research conducted in Tanah Datar District identifies several parameters associated with midwife performance: Length of service, supervision by coordinating midwives, motivation, and job satisfaction [20]. The suboptimal performance of midwifery services in South Aceh Regency can be attributed to insufficient guidance from the Health Office, as well as low levels of knowledge and motivation among midwives [21]. Research in Bangli Regency demonstrates a significant relationship between the performance of village midwives and factors such as competence, financial compensation, and supervision. Among these parameters, supervision has the most substantial impact, influencing midwife performance 25 times more than the other factors. Adiputri et al.'s research [22] in Semarang reveals that facilitative supervision lacked formal preparation, consisting only of an assignment letter and a checklist. Both Bikor and PMB had not received specialized training or socialization related to facilitative supervision. Instead, Bikor was provided solely with a checklist by the Health Office as an assessment guideline, without a reference book for facilitative supervision. Additionally, orientation on the checklist for PMB was not conducted for all Bikors. Consequently, critical components of facilitative supervision, such as self-assessment by PMB and verification by Bikor in collaboration with PMB, were not implemented. As a result, follow-up supervision was solely based on Bikors' assessments. Supervision often took the form of unscheduled inspections without prior agreement on the implementation schedule with PMB, occurring during working hours at the Public Health Center.
To enhance the performance and professionalism of midwives, mentoring relationships are crucial for developing professional confidence. These relationships should be structured with clear duration and agreements. Mentors are responsible for listening, challenging, supporting, and guiding their mentees, fostering research, exploration, and reflective practice. While the mentored midwife retains responsibility for her practice and obligations, senior midwives or mentors play a key role in guiding less experienced colleagues to improve performance, service quality, and address areas of poor performance. Performance supervision can be conducted through supportive, statutory, and professional supervision methods [23].
Research conducted in Belgium examine the relationship between advanced midwifery practitioners' task performance and their competencies across various domains. The study found that certain tasks, such as research and clinical expertise, were performed inadequately. This underperformance was attributed to factors related to work organization, competency deficiencies, and insufficient leadership [24]. Research in Ethiopia express that autocratic leadership is the most common style among midwifery leaders and has a negative effect on midwives' performance. Democratic and laissez-faire leadership styles are associated with improved performance [25]. Research in Sudan indicates that supervision of midwives can significantly enhance service quality. It also aids in developing robust supervision systems, increases active engagement within the community, and strengthens the relationships between health facilities and midwives. Additionally, effective supervision can boost public trust in midwives [26-29].
Study limitation
The strict inclusion criteria may limit the generalizability of the study's findings. For instance, only midwives with more than two years of experience were included, potentially excluding insights into the performance of newer midwives or those with differing professional backgrounds. Additionally, participant selection based on Health Office data and village mapping could introduce bias if the data is incomplete or inaccurate, which may affect the overall representativeness of the sample.
Strength and recommendation
This research is highly relevant to the local context of Muaro Jambi, offering valuable insights for policy development and improved planning of public health programs in the region. The study also provides recommendations for fostering partnerships between the government, educational institutions, and health organizations to support training and professional development initiatives for village midwives.
Conclusion
Age and education level are key determinants of village midwives' performance in maternal and child health services.
Acknowledgments: The authors would like to thank all participants for their participation and cooperation throughout the study. They also thank the Faculty of Public Health of the University of Indonesia and the Health Polytechnic of the Jambi Ministry of Health for their support and assistance.
Ethical Permissions: Prior to data collection, all participants signed an informed consent form, and the research ethics committee of Universitas Jambi, Indonesia, granted permission to perform this study (Number: 572/UN21.8/PT.01.04/2024).
Conflicts of Interests: None declared.
Authors' Contribution: Ruwayda R (First Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Methodologist/Discussion Writer/Statistical Analyst (40%); Hastono SP (Second Author), Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (20%); Siregar KN (Third Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (20%); Martha E (Fourth Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (10%); Nurdini L (Fifth Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (10%)
Funding/Support: None Funding.
Article Type: Descriptive & Survey |
Subject:
Social Determinants of Health
Received: 2024/11/7 | Accepted: 2024/12/6 | Published: 2024/12/10
Received: 2024/11/7 | Accepted: 2024/12/6 | Published: 2024/12/10
References
1. WHO. Maternal death surveillance and response: Technical guidance: Information for action to prevent maternal death. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. [Link]
2. Nove A, Friberg IK, De Bernis L, McConville F, Moran AC, Najjemba M, et al. Potential impact of midwives in preventing and reducing maternal and neonatal mortality and stillbirths: A lives saved tool modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2021;9(1):e24-32. [Link] [DOI:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30397-1]
3. WHO. Strengthening quality midwifery education for universal health coverage 2030: Framework for action. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. [Link]
4. WHO. Maternal mortality [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024 [cited 2024, April, 26]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality. [Link]
5. Kemenkes RI. Indonesia health profile 2021. Jakarta: Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia; 2022. [Indonesian] [Link]
6. McCarthy J, Maine D. A framework for analyzing the determinants of maternal mortality. Stud Fam Plann. 1992;23(1):23-33. [Link] [DOI:10.2307/1966825]
7. WHO. Nursing and midwifery [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024 [cited 2024, May, 3]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/nursing-and-midwifery. [Link]
8. Okereke E, Ishaku SM, Unumeri G, Mohammed B, Ahonsi B. Reducing maternal and newborn mortality in Nigeria-A qualitative study of stakeholders' perceptions about the performance of community health workers and the introduction of community midwifery at primary healthcare level. Hum Resour Health. 2019;17(1):102. [Link] [DOI:10.1186/s12960-019-0430-0]
9. Pappu NI, Öberg I, Byrskog U, Raha P, Moni R, Akhtar S, et al. The commitment to a midwifery centre care model in Bangladesh: An interview study with midwives, educators and students. PLoS One. 2023;18(4):e0271867. [Link] [DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0271867]
10. Musaddiq T. The impact of community midwives on maternal healthcare utilization. Health Econ. 2022;32(3):697-714. [Link] [DOI:10.1002/hec.4640]
11. Nallala S, Ghosh U, Desaraju SS, Kadam S, Kadarpeta RR, Van Belle S. Why are they "unreached"? Macro and Meso determinants of health care access in hard to reach areas of Odisha, India. Int J Equity Health. 2023;22(1):2. [Link] [DOI:10.1186/s12939-022-01817-y]
12. D'Ambruoso L, Achadi E, Adisasmita A, Izati Y, Makowiecka K, Hussein J. Assessing quality of care provided by Indonesian village midwives with a confidential enquiry. Midwifery. 2009;25(5):528-39. [Link] [DOI:10.1016/j.midw.2007.08.008]
13. Triyana M. The effects of Indonesia's 'midwife in the village' programme 10 years post-launch. Popul Stud. 2016;70(3):365-76. [Link] [DOI:10.1080/00324728.2016.1145728]
14. Lindgren H, Bogren M, Osika Friberg I, Berg M, Hök G, Erlandsson K. The midwife's role in achieving the sustainable development goals: Protect and invest together-the Swedish example. Glob Health Action. 2022;15(1):2051222. [Link] [DOI:10.1080/16549716.2022.2051222]
15. Harvey G, Kelly J, Kitson A, Thornton K, Owen V. Leadership for evidence-based practice-Enforcing or enabling implementation?. Collegian. 2020;27(1):57-62. [Link] [DOI:10.1016/j.colegn.2019.04.004]
16. Yunita H, Kuntjoro T, Purnami CT. Factors affecting village midwives work performance in conducting early detection of high risk pregnancy in the antenatal care in south Bengkulu district. J Indones Health Manag. 2013;1(2):79-88. [Indonesian] [Link]
17. Mirdahni R, Kintoko Rochadi R, Arma AJA. Factors that influence the performance of midwives in implementing standard antenatal services in the work area of the Pidie Health Center. SERAMBI SAINTIA: JURNAL SAINS DAN APLIKASI. 2021;9(1):40-8. [Indonesian] [Link]
18. Mwakawanga DL, Rimoy M, Mwanga F, Massae AF, Mushy SE, Kisaka L, et al. Strengthening midwives' competencies for addressing maternal and newborn mortality in Tanzania: Lessons from Midwifery Emergency Skills Training (MEST) project. Midwifery. 2023;122:103695. [Link] [DOI:10.1016/j.midw.2023.103695]
19. Asnawi A, Wungouw EE, Kerong IH, Butu Y, Labo I, impson L. Knowledge and skills of coordinator midwives and midwives in NTT. Australia Indonesia Partnership for Maternal and Neonatal Health; 2017. [Indonesian] [Link]
20. Yarnita Y. Factors related to village midwife performance in efforts to reduce neonatal mortality in Tanah Datar district. Glob Health J. 2020;3(3):100-8. [Indonesian] [Link] [DOI:10.33085/jkg.v3i3.4676]
21. Husna A, Besral B. Performance of village midwives in the health care guarantee program for the poor. KESMAS. 2009;4(1):18-23. [Indonesian] [Link] [DOI:10.21109/kesmas.v4i1.196]
22. Adiputri A, Wijaya IPG, Karmaya INM. The competency, financial compensation, supervision and performance of the village midwives in the Bangli regency. Public Health Prev Med Arch. 2014;2(1):76-80. [Indonesian] [Link] [DOI:10.53638/phpma.2014.v2.i1.p14]
23. International Confederation of Midwives [Internet]. Mentoring Guidelines for Midwives. Cent Mentor Excell. 2020;39:12. [cited 2020, Januari, 5]. Available from: https://internationalmidwives.org/resources/mentoring-guidelines-for-midwives/ [Link]
24. Van Hecke A, Goemaes R, Verhaeghe S, Beyers W, Decoene E, Beeckman D. Leadership in nursing and midwifery: Activities and associated competencies of advanced practice nurses and midwives. J Nurs Manag. 2019;27(6):1261-74. [Link] [DOI:10.1111/jonm.12808]
25. Fenta Kebede B, Aboye T, Dagnaw Genie Y, Tesfa TB, Yetwale Hiwot A. The effect of leadership style on midwives' performance, southwest, Ethiopia. J Healthc Leadersh. 2023;15:31-41. [Link] [DOI:10.2147/JHL.S397907]
26. Ma'rufi I, Ningtyias FW, Mardiyanti M. The influence of knowledge, motivation, leadership, and workload toward public health center midwives' performance in facilitative supervision of MCH program in Lumajang district. Health Notions. 2018;2(4):478-82. [Link]
27. WHO. Web appendix. Mapping of WHO competencies for the maternal and newborn health (MNH) professional based on previously published international standards. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. [Link]
28. Chen S, Wang R, Xu N, Zhang J, Liu Y, Cong S, et al. Identification of factors influencing core competence promotion among professional nurses and midwives: A qualitative study using the COM-B model. Nurse Educ Pract. 2023;69:103619. [Link] [DOI:10.1016/j.nepr.2023.103619]
29. Michie S, Van Stralen MM, West R. The behaviour change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement Sci. 2011;6(1):42. [Link] [DOI:10.1186/1748-5908-6-42]
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |






