Volume 11, Issue 3 (2023)
Health Educ Health Promot 2023, 11(3): 499-505 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Taha A, Shratooh S, Jasim A. Limnological Properties of Euphrates River in AL-Anbar Province, Iraq. Health Educ Health Promot 2023; 11 (3) :499-505
URL: http://hehp.modares.ac.ir/article-5-60232-en.html
URL: http://hehp.modares.ac.ir/article-5-60232-en.html
1- Department of Biology, Anbar Education Directorate, Ramadi, Iraq
2- Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Anbar, Ramadi, Iraq
3- Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Baghdad, Iraq
2- Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Anbar, Ramadi, Iraq
3- Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Baghdad, Iraq
Keywords: Pollution [MeSH], Physiochemical Characteristics [MeSH], Euphrates [MeSH], Discharges [MeSH]
Full-Text [PDF 744 kb]
(4306 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (1781 Views)
Full-Text: (538 Views)
Introduction
Rivers are still the main source of human water; rivers receive and mitigate pollutants from various human activities [1] because most water uses are non-use consumption, and a large proportion of the water may return to the water source [2]. Such pollutants cause the form of heavy water laden with several pollutants, the proportion of which increases with the elevation of population, urban and industrial development, and the increase of agricultural activities [2, 3]. The degree of electrical conductivity, total dissolved substances, salinity, and hardness may vary according to the dose of such contamination in the river, causing crucial changes in the ecological ecosystem balance in these waters [4, 5]. Several studies refer to the role of these limnological variables and their impact on the water body. In a study on the Euphrates River in the province of Babil, it was found that the concentrations of chloride ions and calcium sulfate, as well as hardness and turbidity, increased as they exceeded the permissible limits for drinking water. In contrast, the elements of lead, cadmium, nickel, copper and zinc did not exceed the internationally permissible values [6]. Another study showed pollution of the river with cadmium. In the Euphrates basin from Heet City to Ramadi City, high turbidity, electrical conductivity, and calcium, sodium, and chlorine concentrations were observed. Still, it did not exceed the standard limits [7]. Also, the influence of Wadi Hajlan Springs resulted in huge changes in water properties via the pollutants added to these ecosystems [8]. A recent study of the quality of Euphrates River water within the city of Ramadi and Lake of Habbaniyah found that the electrical conductivity values and the concentration of chloride, sodium, and sulfate ions increased compared with the concentrations of calcium, magnesium, and potassium, while the concentration of phosphate, ammonium and nitrate ions in the river water was within the standard limits. However, the influents discharged directly into the river from human activities are the reason behind such raised concentrations [9-11].
Hassan et al. evaluated the environmental monitoring program for natural rivers about the condition of the Euphrates River. They found that it was within the permissible limits in the northern part of the river. At the same time, a rise in the values (TDS, TSS, EC) appeared above the permissible limits in the southern part of the river to Qurna, and the results of the chemical analysis of the river water showed that it was within the Iraqi and international standard specifications in the northern part. In contrast, the southern part of the river was higher than the Iraqi and international specifications, beside the quality of the river water in the northern part was sulfur [12]. The same conditions were found in another similar study about phytoplankton's spatial and temporal distribution affected by related physical and chemical variables in the Al-Abasia side river branched from Euphrates [13].
Scientific studies indicate that any water body's physical and chemical characteristics are closely related to the life of various organisms that depend on this type of water [14, 15]. Nevertheless, studying these characteristics gives an idea of choosing the appropriate method for treating this water preparing it for drinking, and determining its suitability for human uses in various fields such as industry and agriculture [16]. These characteristics have a major role in the biodiversity of water bodies, as they contribute to the abundance of certain organisms and the disappearance of other organisms that may have an important role in the fixation of dissolved oxygen necessary for the oxidation of organic matter by microorganisms, and thus influence the values of the biological requirement for oxygen, which is an important criterion in detecting the degree of pollution of this river [17-19].
Instrument and Methods
All work methods were carried out according to APHA [20] and Abbawi & Hassan [21] in all seasons from April 2022 to March 2023.
Study area
The study area is located within the borders of Anbar Province, including Ramadi, Al-Qaim, Anah, Haditha, and Heet cities. Yet, these cities were chosen precisely because they are located on both sides of the Euphrates River, which has a high population density and has an important impact on the river's physical and chemical characteristics due to the large number of different human activities in these cities on the one hand, and the lack of recent studies on them on the other hand [22]. Water samples in three replicates were taken from the river through each city. The first sample is before the river enters the city, the second is during the river's entry into the city, and the third is after the river passes the city. The sample represents each section of the river within the city, randomly located between the city of Ramadi and the city of Al-Qaim (Figure 1).
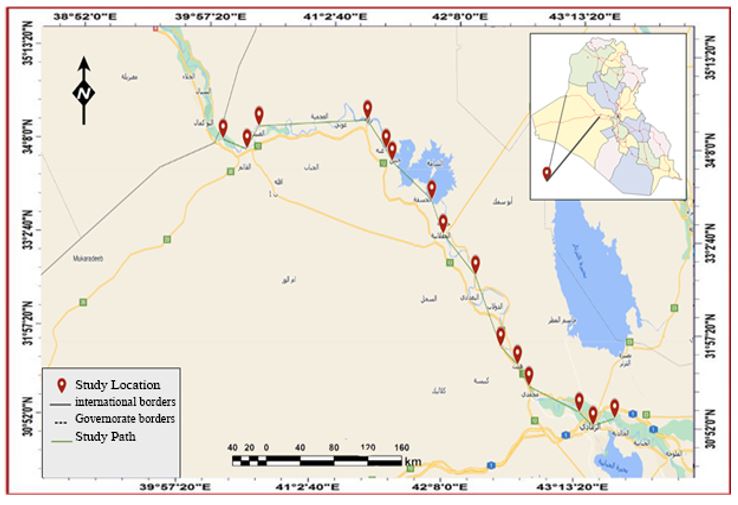
Figure 1. The study sites on the Euphrates River
Physical and chemical properties
The water temperature was measured in situ using a mercury thermometer. Also, the electrical conductivity was measured by an electrical conductivity meter (HANNA-110) after calibration with standard solutions, and the results were reported as µs/cm. The salinity was calculated from the electrical conductivity values using the following equation [23].

The pH values and total dissolved solids were measured directly in the field using a pH meter (HANNA-112G multimeter device) after calibration with standard solutions; the results were expressed in (mg/l). As for the total suspended solids were measured in the laboratory by filtering 100ml of the sample through a filter paper of 0.45µ after being weighed accurately (B). This paper was dried using an oven at 103-105°C for 24 hours, after that it was weighed (A), and the results were expressed in mg/l.
TSS (mg/L) = (A-B) × 100/Volume of sample (ml)
Where:
A: Weight of the paper and dissolved solids in grams.
B: weight of the paper in grams.
As for the sulfate examination, the method of burning the sediment by weight was followed, where sulfate precipitates at the boiling point and in the presence of hydrochloric acid in the form of barium sulfate by adding barium chloride. To find the sulfate concentration, the precipitate was filtered and burned; then its weight was accurately determined using the following equation:
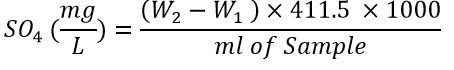
Where:
W2= Weight of the slurry with the sediment
W1= Empty weight of the slurry
Whilst for estimating the chloride ion concentration, the leaching method was used with silver nitrate, and the results were expressed in mg/liter units.

Where:
A: Standard volume of silver nitrate used to purge the sample (ml)
B: Standard volume of silver nitrate used for dissolving in distilled water (ml)
N: Standard silver nitrate solution.
As for the determination of bicarbonate, the phenolphthalein method was followed, where 100ml of the sample was flushed with sodium hydroxide solution (0.02N), and the results were expressed in mg/l units.
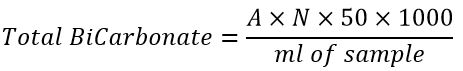
Where:
A: The volume of sodium hydroxide used for emollients
N: NaOH nM (0.02N)
As for the determination of the calcium ion concentration, it is done by EDTA titration method, as follows:

Where:
A: volume of Na2EDTA used for calibration
B: mg CaCO3 equivalent to ml of EDTA solution
Additionally, the estimation of sodium concentration is done using a Flam spectrophotometer (GS 900).
Statistical Analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the LSD tests were used to compare significant differences at the level of 0.05, as well as the Pearson correlation coefficient in SPSS 25 software.
Findings
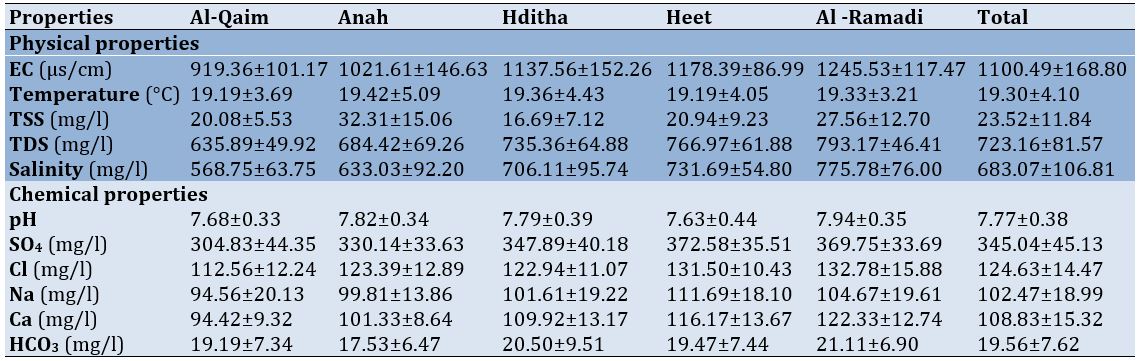
The average water temperature of the Euphrates River was 19.33±3.21°C at Al-Ramadi station and 19.19±3.69°C at Al-Qaim station. The highest conductivity mean was in Al-Ramadi, known for its high salinity (775.78mg/l). The total hardness did not exceed the mean of total suspended solids in the study areas and was 16.69mg/l in the Haditha station, while the ratio increased to 32.31mg/l in Anah. SO4 reached 372.58mg/l in the Heet, while it reached 304.83mg/l in Al-Qaim. The highest mean of Cl was in the Ramadi (132.78mg/l), and the lowest was 112.56mg/l in the Al-Qaim. The highest mean of Sodium was in Heet (111.69mg/l), and the lowest was 94.5mg/l in Al Qaim (Table 1).
Table 1. Mean values of physical and chemical properties for the studied sites
The pH results showed statistically significant differences between months (p<0.05). The chloride ion's highest mean was in July (140.2mg/l), and the lowest appeared in January (112mg/l; p<0.05). For Sodium, the highest mean was in October (126.5mg/l), and the lowest was in January (71.6mg/l; p<0.05). Ca highest mean was in October (125.6mg/l), and its lowest was 95.27mg/l in January (p<0.05). HCO3's highest mean was in May (33mg/l), and the lowest was in February (11.6mg/l). The highest mean temperature was recorded in July (26.26°C), and the lowest was in January (13.2°C; Table 2).
Table 2. Mean of the chemical and physical properties of the Euphrates River according to months

The Pearson correlation coefficient was performed between the physical and chemical properties (Table 3).
Table 3. Correlation coefficient of the physical and chemical properties of the Euphrates River

Discussion
The variation in water temperature is related to many environmental factors such as water flow, water depth, bottom material, internal water temperature, exposure to direct sunlight, the degree of deformation, and, most importantly, the air temperature [2]—local variation in water temperature due to the difference in measurement time. Similar conclusions were reported by other authors [24, 25]. Water temperature affects the solubility of gases and salts in water and thus plays a key role in determining many physical and chemical properties. Living organisms differ in how much they tolerate heat; some can withstand a wide range of temperatures, while others live in a narrow range. Water bodies are divided into layers according to the temperature in the water column, known as thermal stratification. This feature appears clearly in ocean waters, seas, and lakes, to a lesser extent, in running water due to mixing processes during the movement of rivers and streams towards their mouths [18, 26].
Conductivity refers to the dissolved salts in the water due to the correlation between TDS and EC; the results are consistent with similar studies [27]. From the aforementioned, we find a difference between our results and those contained in previous studies. This is due to the difference in the modeling period, which was limited in previous studies to one or two times and did not take into account sampling during a water year, which may reflect a change in the discharge of river water and the amount of dissolved salts [28, 29]. When comparing the electrical conductivity values in our current study with the national and international standards for water quality suitable for the aquatic environment, we find that they have exceeded the permissible limits (400µs/cm) [30, 31]. As for the results of the suspended solids TSS, it is consistent with what was reached by [6, 24], where they noticed that there is a clear decrease in the city of Heet compared to the rest of the study areas, while the results of the current study did not agree with a number of researchers who confirmed the presence of high concentrations during the winter and high concentrations of Low during the summer season. This is probably related to low water concentration, high evapotranspiration during autumn and summer, and the shallow neck. In contrast, the precipitation rate and mitigation factor in winter and late autumn cause a decrease in TSS and TDS [13, 32]. As for the dissolved solids TDS, when comparing their concentrations with the national and international standards, we find that they did not exceed the permissible limits (1500ml/L). Also, it was found that the TDS values did not exceed the permissible limits for the city of Ramadi. They indicated that total dissolved salts and electrical conductivity values did not exceed the permissible limits. Still, the TDS value increased in both periods [7] due to the spring eyes. Still, Ali & Al-Shandah [8] found that the amount of TDS did not exceed the permissible limits in the northern part of the river. Still, it is higher in the southern part of the river, where the highest value was recorded in the city of Ramadi, and the lowest value in the city of Al-Qaim, and the reason for that is attributed to the lack of a source of sewage. Similar results have been reported by other studies [25, 26].
The current study showed that the recorded pH values were within their narrow range and tended to be slightly alkaline, as is common in Iraqi inland waters. This is due to the buffering capacity of Iraqi natural waters due to the high content of calcium bicarbonate [15]. However, the pH ranges in most natural waters between 4-9, and dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and ammonia significantly lower the pH values [10]. The results of the current study agreed with previous studies on the light alkalinity of the inland surface waters in Iraq due to the abundance of bicarbonate and carbonate ions [17, 32]. No significant differences were observed in the pH values of the study stations, as these values ranged within a narrow range due to the high regulating ability of the basal water rich in bicarbonates. The high values of pH during the autumn season are due to the high density of phytoplankton during this season and, thus, the increase in the effectiveness of photosynthesis that leads to the consumption of carbon dioxide and an increase in the pH [12].
The values of sulfate ion concentrations rise in the Heet region. This rise is attributed to the effect of the sulfur springs in Heet. The results of the current study were close to the results reached by [33]. Still, another study found that the concentration of sulfate ions exceeded the permissible limit, as well as a significant increase in the concentration of the sulfate ion in Heat, as recorded by [7] an increase in the concentration of the sulfate ion, where the highest concentration was recorded in the Baghdadi region, and attributed the reason to the storage period in Haditha Lake, the sulfur springs that feed the river, the high temperatures in summer, and the increase in evaporation increases the concentration of the sulfate ion [17]. The sulfate ion is present in industrial water, such as the battery industry, the sulfuric acid industry, food industries, and oil refining operations. Still, it is not found on the banks of the Euphrates River. A study [23] indicated that the sulfate ion concentration was high in the northern part of the Euphrates River and higher in the southern part. It attributed the reason for the difference to several factors, the most important of which is the geological factor [22].
The World Health Organization has not set a standard for the permissible concentration of chloride ions, nor has the US Environmental Protection Agency. When comparing the chloride ion concentration of the Euphrates River water within the study area and during the study period, we find it within the permissible limits according to Canadian standards (251ml/L). The highest concentration of chloride ions was in July. The reason is attributed to the increase in the concentration of chloride ions with the rise in temperature due to the process of water evaporation, which is consistent with the findings of [34]. Yet, it was found that the chloride ion values in the Euphrates River are within the permissible limits, but they are much higher than the waters of the world's rivers. However, it was the highest value in the city of Ramadi and Heet, which are agricultural areas. The sewage water, agricultural land irrigation water, and industrial wastewater are sources of increasing the percentage of chloride ions in the river water. At the same time, it was of less value in the city of Al-Qaim, as the river has the ability to self-purify [7].
The average sodium ion concentration did not exceed the permissible limits according to the standards of the World Health Organization (200ml/L). When comparing the sodium concentration in the current study with the results of previous studies, we notice that there is no difference with the findings of Ali & Al-Shandah [8], indicated that the sodium concentration of the Euphrates River water was (185ml/L) within the areas of Ramadi and Fallujah, while the study concluded that the average sodium ion concentration of the Euphrates River water within the study area located between Al-Qaim and Qurna was (113.5ml/L) [35, 36]. The study by Abdulrahman et al. found that the average sodium ion concentration of the Euphrates River water within the Heet region reached (93ml/L), meaning it did not exceed the permissible limits. It was found that the sodium ion concentration of the Euphrates River water from Al-Qaim to Al-Baghdadi ranged between (50.5-52ml/L) [7]. The obvious reason for the difference in results between the current study and other studies is that previous studies did not take a water year when conducting the study, in addition to the river level was low throughout the study period compared to previous studies. Studies by the World Health Organization consider sewage and industrial water an additional source of sodium in healthy water. Therefore, we see that the source of sodium ions in the river water within the study area is a natural source, which is the dissolution of minerals containing sodium in their composition, such as plagioclase [22].
High concentrations of the bicarbonate ion were recorded, and this may be due to a decrease in the water level in the river and the discharge rate, which increases evaporation rates and thus increases the amount of salts, and this is consistent with what was reached by [37]. In contrast, the agricultural activity during the Sihud period affected the concentration of bicarbonate ion in the Sihud period, while the study showed a fluctuation in the concentration of bicarbonate, as the lowest value was recorded in Anah City. The highest value in Haditha city. found that the high bicarbonate in Heet is due to the effect of the springs of Heet in the region. Likewise, the results of a similar study are identical to what we have reached in the current study, as the concentration of the bicarbonate ion did not exceed the permissible limits [6, 7, 37].
Conclusion
The water of the Euphrates River is exposed to pollution due to various wastes that are constantly dumped on the banks and course of the Euphrates River within the study area, especially the cities of Ramadi and Heet, as they are the largest and most densely populated cities. The water quality of the Euphrates River is considered to be of simple alkalinity based on the pH values.
Acknowledgments: I extend my sincere thanks to Anbar University - College of Science and to the Anbar Environment Directorate - Great Anbar Water Project for preparing all the laboratories for me to conduct physical, chemical and biological tests for a research project and providing all the supplies, equipment and materials needed to complete this research. With great appreciation and respect.
Ethical Permission: We did not need any ethical request because we did not take blood samples from humans or animals, but rather samples were collected from the water of the Euphrates River.
Conflict of Interests: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Authors’ Contribution: Taha AMA (First Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (45%); Shratooh SM (Second Author), Introduction Writer/Assistant Researcher (30%); Jasim AH (Third Author), Methodologist/Assistant Researcher/Statistical Analyst (30%)
Funding/Support: It was done at personal expense.
Rivers are still the main source of human water; rivers receive and mitigate pollutants from various human activities [1] because most water uses are non-use consumption, and a large proportion of the water may return to the water source [2]. Such pollutants cause the form of heavy water laden with several pollutants, the proportion of which increases with the elevation of population, urban and industrial development, and the increase of agricultural activities [2, 3]. The degree of electrical conductivity, total dissolved substances, salinity, and hardness may vary according to the dose of such contamination in the river, causing crucial changes in the ecological ecosystem balance in these waters [4, 5]. Several studies refer to the role of these limnological variables and their impact on the water body. In a study on the Euphrates River in the province of Babil, it was found that the concentrations of chloride ions and calcium sulfate, as well as hardness and turbidity, increased as they exceeded the permissible limits for drinking water. In contrast, the elements of lead, cadmium, nickel, copper and zinc did not exceed the internationally permissible values [6]. Another study showed pollution of the river with cadmium. In the Euphrates basin from Heet City to Ramadi City, high turbidity, electrical conductivity, and calcium, sodium, and chlorine concentrations were observed. Still, it did not exceed the standard limits [7]. Also, the influence of Wadi Hajlan Springs resulted in huge changes in water properties via the pollutants added to these ecosystems [8]. A recent study of the quality of Euphrates River water within the city of Ramadi and Lake of Habbaniyah found that the electrical conductivity values and the concentration of chloride, sodium, and sulfate ions increased compared with the concentrations of calcium, magnesium, and potassium, while the concentration of phosphate, ammonium and nitrate ions in the river water was within the standard limits. However, the influents discharged directly into the river from human activities are the reason behind such raised concentrations [9-11].
Hassan et al. evaluated the environmental monitoring program for natural rivers about the condition of the Euphrates River. They found that it was within the permissible limits in the northern part of the river. At the same time, a rise in the values (TDS, TSS, EC) appeared above the permissible limits in the southern part of the river to Qurna, and the results of the chemical analysis of the river water showed that it was within the Iraqi and international standard specifications in the northern part. In contrast, the southern part of the river was higher than the Iraqi and international specifications, beside the quality of the river water in the northern part was sulfur [12]. The same conditions were found in another similar study about phytoplankton's spatial and temporal distribution affected by related physical and chemical variables in the Al-Abasia side river branched from Euphrates [13].
Scientific studies indicate that any water body's physical and chemical characteristics are closely related to the life of various organisms that depend on this type of water [14, 15]. Nevertheless, studying these characteristics gives an idea of choosing the appropriate method for treating this water preparing it for drinking, and determining its suitability for human uses in various fields such as industry and agriculture [16]. These characteristics have a major role in the biodiversity of water bodies, as they contribute to the abundance of certain organisms and the disappearance of other organisms that may have an important role in the fixation of dissolved oxygen necessary for the oxidation of organic matter by microorganisms, and thus influence the values of the biological requirement for oxygen, which is an important criterion in detecting the degree of pollution of this river [17-19].
Instrument and Methods
All work methods were carried out according to APHA [20] and Abbawi & Hassan [21] in all seasons from April 2022 to March 2023.
Study area
The study area is located within the borders of Anbar Province, including Ramadi, Al-Qaim, Anah, Haditha, and Heet cities. Yet, these cities were chosen precisely because they are located on both sides of the Euphrates River, which has a high population density and has an important impact on the river's physical and chemical characteristics due to the large number of different human activities in these cities on the one hand, and the lack of recent studies on them on the other hand [22]. Water samples in three replicates were taken from the river through each city. The first sample is before the river enters the city, the second is during the river's entry into the city, and the third is after the river passes the city. The sample represents each section of the river within the city, randomly located between the city of Ramadi and the city of Al-Qaim (Figure 1).

Figure 1. The study sites on the Euphrates River
Physical and chemical properties
The water temperature was measured in situ using a mercury thermometer. Also, the electrical conductivity was measured by an electrical conductivity meter (HANNA-110) after calibration with standard solutions, and the results were reported as µs/cm. The salinity was calculated from the electrical conductivity values using the following equation [23].

The pH values and total dissolved solids were measured directly in the field using a pH meter (HANNA-112G multimeter device) after calibration with standard solutions; the results were expressed in (mg/l). As for the total suspended solids were measured in the laboratory by filtering 100ml of the sample through a filter paper of 0.45µ after being weighed accurately (B). This paper was dried using an oven at 103-105°C for 24 hours, after that it was weighed (A), and the results were expressed in mg/l.
TSS (mg/L) = (A-B) × 100/Volume of sample (ml)
Where:
A: Weight of the paper and dissolved solids in grams.
B: weight of the paper in grams.
As for the sulfate examination, the method of burning the sediment by weight was followed, where sulfate precipitates at the boiling point and in the presence of hydrochloric acid in the form of barium sulfate by adding barium chloride. To find the sulfate concentration, the precipitate was filtered and burned; then its weight was accurately determined using the following equation:
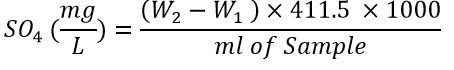
Where:
W2= Weight of the slurry with the sediment
W1= Empty weight of the slurry
Whilst for estimating the chloride ion concentration, the leaching method was used with silver nitrate, and the results were expressed in mg/liter units.

Where:
A: Standard volume of silver nitrate used to purge the sample (ml)
B: Standard volume of silver nitrate used for dissolving in distilled water (ml)
N: Standard silver nitrate solution.
As for the determination of bicarbonate, the phenolphthalein method was followed, where 100ml of the sample was flushed with sodium hydroxide solution (0.02N), and the results were expressed in mg/l units.
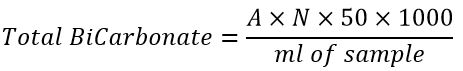
Where:
A: The volume of sodium hydroxide used for emollients
N: NaOH nM (0.02N)
As for the determination of the calcium ion concentration, it is done by EDTA titration method, as follows:

Where:
A: volume of Na2EDTA used for calibration
B: mg CaCO3 equivalent to ml of EDTA solution
Additionally, the estimation of sodium concentration is done using a Flam spectrophotometer (GS 900).
Statistical Analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the LSD tests were used to compare significant differences at the level of 0.05, as well as the Pearson correlation coefficient in SPSS 25 software.
Findings
The average water temperature of the Euphrates River was 19.33±3.21°C at Al-Ramadi station and 19.19±3.69°C at Al-Qaim station. The highest conductivity mean was in Al-Ramadi, known for its high salinity (775.78mg/l). The total hardness did not exceed the mean of total suspended solids in the study areas and was 16.69mg/l in the Haditha station, while the ratio increased to 32.31mg/l in Anah. SO4 reached 372.58mg/l in the Heet, while it reached 304.83mg/l in Al-Qaim. The highest mean of Cl was in the Ramadi (132.78mg/l), and the lowest was 112.56mg/l in the Al-Qaim. The highest mean of Sodium was in Heet (111.69mg/l), and the lowest was 94.5mg/l in Al Qaim (Table 1).
Table 1. Mean values of physical and chemical properties for the studied sites

The pH results showed statistically significant differences between months (p<0.05). The chloride ion's highest mean was in July (140.2mg/l), and the lowest appeared in January (112mg/l; p<0.05). For Sodium, the highest mean was in October (126.5mg/l), and the lowest was in January (71.6mg/l; p<0.05). Ca highest mean was in October (125.6mg/l), and its lowest was 95.27mg/l in January (p<0.05). HCO3's highest mean was in May (33mg/l), and the lowest was in February (11.6mg/l). The highest mean temperature was recorded in July (26.26°C), and the lowest was in January (13.2°C; Table 2).
Table 2. Mean of the chemical and physical properties of the Euphrates River according to months

The Pearson correlation coefficient was performed between the physical and chemical properties (Table 3).
Table 3. Correlation coefficient of the physical and chemical properties of the Euphrates River

Discussion
The variation in water temperature is related to many environmental factors such as water flow, water depth, bottom material, internal water temperature, exposure to direct sunlight, the degree of deformation, and, most importantly, the air temperature [2]—local variation in water temperature due to the difference in measurement time. Similar conclusions were reported by other authors [24, 25]. Water temperature affects the solubility of gases and salts in water and thus plays a key role in determining many physical and chemical properties. Living organisms differ in how much they tolerate heat; some can withstand a wide range of temperatures, while others live in a narrow range. Water bodies are divided into layers according to the temperature in the water column, known as thermal stratification. This feature appears clearly in ocean waters, seas, and lakes, to a lesser extent, in running water due to mixing processes during the movement of rivers and streams towards their mouths [18, 26].
Conductivity refers to the dissolved salts in the water due to the correlation between TDS and EC; the results are consistent with similar studies [27]. From the aforementioned, we find a difference between our results and those contained in previous studies. This is due to the difference in the modeling period, which was limited in previous studies to one or two times and did not take into account sampling during a water year, which may reflect a change in the discharge of river water and the amount of dissolved salts [28, 29]. When comparing the electrical conductivity values in our current study with the national and international standards for water quality suitable for the aquatic environment, we find that they have exceeded the permissible limits (400µs/cm) [30, 31]. As for the results of the suspended solids TSS, it is consistent with what was reached by [6, 24], where they noticed that there is a clear decrease in the city of Heet compared to the rest of the study areas, while the results of the current study did not agree with a number of researchers who confirmed the presence of high concentrations during the winter and high concentrations of Low during the summer season. This is probably related to low water concentration, high evapotranspiration during autumn and summer, and the shallow neck. In contrast, the precipitation rate and mitigation factor in winter and late autumn cause a decrease in TSS and TDS [13, 32]. As for the dissolved solids TDS, when comparing their concentrations with the national and international standards, we find that they did not exceed the permissible limits (1500ml/L). Also, it was found that the TDS values did not exceed the permissible limits for the city of Ramadi. They indicated that total dissolved salts and electrical conductivity values did not exceed the permissible limits. Still, the TDS value increased in both periods [7] due to the spring eyes. Still, Ali & Al-Shandah [8] found that the amount of TDS did not exceed the permissible limits in the northern part of the river. Still, it is higher in the southern part of the river, where the highest value was recorded in the city of Ramadi, and the lowest value in the city of Al-Qaim, and the reason for that is attributed to the lack of a source of sewage. Similar results have been reported by other studies [25, 26].
The current study showed that the recorded pH values were within their narrow range and tended to be slightly alkaline, as is common in Iraqi inland waters. This is due to the buffering capacity of Iraqi natural waters due to the high content of calcium bicarbonate [15]. However, the pH ranges in most natural waters between 4-9, and dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and ammonia significantly lower the pH values [10]. The results of the current study agreed with previous studies on the light alkalinity of the inland surface waters in Iraq due to the abundance of bicarbonate and carbonate ions [17, 32]. No significant differences were observed in the pH values of the study stations, as these values ranged within a narrow range due to the high regulating ability of the basal water rich in bicarbonates. The high values of pH during the autumn season are due to the high density of phytoplankton during this season and, thus, the increase in the effectiveness of photosynthesis that leads to the consumption of carbon dioxide and an increase in the pH [12].
The values of sulfate ion concentrations rise in the Heet region. This rise is attributed to the effect of the sulfur springs in Heet. The results of the current study were close to the results reached by [33]. Still, another study found that the concentration of sulfate ions exceeded the permissible limit, as well as a significant increase in the concentration of the sulfate ion in Heat, as recorded by [7] an increase in the concentration of the sulfate ion, where the highest concentration was recorded in the Baghdadi region, and attributed the reason to the storage period in Haditha Lake, the sulfur springs that feed the river, the high temperatures in summer, and the increase in evaporation increases the concentration of the sulfate ion [17]. The sulfate ion is present in industrial water, such as the battery industry, the sulfuric acid industry, food industries, and oil refining operations. Still, it is not found on the banks of the Euphrates River. A study [23] indicated that the sulfate ion concentration was high in the northern part of the Euphrates River and higher in the southern part. It attributed the reason for the difference to several factors, the most important of which is the geological factor [22].
The World Health Organization has not set a standard for the permissible concentration of chloride ions, nor has the US Environmental Protection Agency. When comparing the chloride ion concentration of the Euphrates River water within the study area and during the study period, we find it within the permissible limits according to Canadian standards (251ml/L). The highest concentration of chloride ions was in July. The reason is attributed to the increase in the concentration of chloride ions with the rise in temperature due to the process of water evaporation, which is consistent with the findings of [34]. Yet, it was found that the chloride ion values in the Euphrates River are within the permissible limits, but they are much higher than the waters of the world's rivers. However, it was the highest value in the city of Ramadi and Heet, which are agricultural areas. The sewage water, agricultural land irrigation water, and industrial wastewater are sources of increasing the percentage of chloride ions in the river water. At the same time, it was of less value in the city of Al-Qaim, as the river has the ability to self-purify [7].
The average sodium ion concentration did not exceed the permissible limits according to the standards of the World Health Organization (200ml/L). When comparing the sodium concentration in the current study with the results of previous studies, we notice that there is no difference with the findings of Ali & Al-Shandah [8], indicated that the sodium concentration of the Euphrates River water was (185ml/L) within the areas of Ramadi and Fallujah, while the study concluded that the average sodium ion concentration of the Euphrates River water within the study area located between Al-Qaim and Qurna was (113.5ml/L) [35, 36]. The study by Abdulrahman et al. found that the average sodium ion concentration of the Euphrates River water within the Heet region reached (93ml/L), meaning it did not exceed the permissible limits. It was found that the sodium ion concentration of the Euphrates River water from Al-Qaim to Al-Baghdadi ranged between (50.5-52ml/L) [7]. The obvious reason for the difference in results between the current study and other studies is that previous studies did not take a water year when conducting the study, in addition to the river level was low throughout the study period compared to previous studies. Studies by the World Health Organization consider sewage and industrial water an additional source of sodium in healthy water. Therefore, we see that the source of sodium ions in the river water within the study area is a natural source, which is the dissolution of minerals containing sodium in their composition, such as plagioclase [22].
High concentrations of the bicarbonate ion were recorded, and this may be due to a decrease in the water level in the river and the discharge rate, which increases evaporation rates and thus increases the amount of salts, and this is consistent with what was reached by [37]. In contrast, the agricultural activity during the Sihud period affected the concentration of bicarbonate ion in the Sihud period, while the study showed a fluctuation in the concentration of bicarbonate, as the lowest value was recorded in Anah City. The highest value in Haditha city. found that the high bicarbonate in Heet is due to the effect of the springs of Heet in the region. Likewise, the results of a similar study are identical to what we have reached in the current study, as the concentration of the bicarbonate ion did not exceed the permissible limits [6, 7, 37].
Conclusion
The water of the Euphrates River is exposed to pollution due to various wastes that are constantly dumped on the banks and course of the Euphrates River within the study area, especially the cities of Ramadi and Heet, as they are the largest and most densely populated cities. The water quality of the Euphrates River is considered to be of simple alkalinity based on the pH values.
Acknowledgments: I extend my sincere thanks to Anbar University - College of Science and to the Anbar Environment Directorate - Great Anbar Water Project for preparing all the laboratories for me to conduct physical, chemical and biological tests for a research project and providing all the supplies, equipment and materials needed to complete this research. With great appreciation and respect.
Ethical Permission: We did not need any ethical request because we did not take blood samples from humans or animals, but rather samples were collected from the water of the Euphrates River.
Conflict of Interests: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Authors’ Contribution: Taha AMA (First Author), Introduction Writer/Original Researcher/Discussion Writer (45%); Shratooh SM (Second Author), Introduction Writer/Assistant Researcher (30%); Jasim AH (Third Author), Methodologist/Assistant Researcher/Statistical Analyst (30%)
Funding/Support: It was done at personal expense.
Article Type: Descriptive & Survey |
Subject:
Health Education and Health Behavior
Received: 2023/06/10 | Accepted: 2023/07/16 | Published: 2023/08/2
Received: 2023/06/10 | Accepted: 2023/07/16 | Published: 2023/08/2
References
1. World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking-water quality [Internet]. Geneva: WHO; 2004- [cited 2004 March 14]. Available from: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/42852. [Link]
2. Salah E, Obaid K. Water quality of Euphrates river in Ammereate Al-Falujah city and effect of the anthropogenic activities on it. J Univ Anbar Pure Sci. 2015;9(1):82-93. [Link] [DOI:10.37652/juaps.2015.124386]
3. Hacioglu N, Dulger B. Monthly variation of some physico-chemical and microbiological parameters in Biga Stream (Biga, Canakkale, Turkey). African J Biotechnol. 2009;8(9):12-6. [Link]
4. Hacioglu N, Dulger B. Monthly variation of some physico-chemical and microbiological parameters in Saricay Stream (Canakkale, Turkey). Fresenius Environ Bulletin. 2010;19(5a):986-90. [Link]
5. Ahipathy MV, Puttaiah ET. Ecological characteristics of vrishabhavathy River in Bangalore (India). Environ Geol. 2006;49(8):1217-22. [Link] [DOI:10.1007/s00254-005-0166-0]
6. Al-Heety E, Turky A, Al-Othman E. Physico-chemical assessment of Euphrates river between Heet and Ramadi cities, Iraq. J Water Resour Protection. 2011;3(11):812-23. [Link] [DOI:10.4236/jwarp.2011.311091]
7. Abdulrahman MF, Yosif YM, Saod WM, Al-Heety EA. Effect of discharge on water quality in Euphrates River between Heet and Ramadi, Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2021;5:101-11. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.54.2B.9Ms-2021-08-29]
8. Ali Sf, Al-Shandah BT. Estimation of some plant nutrients and heavy metals in Euphrates river at the cities of Ramadi and Khalidiah. Pollut Res. 2021;40(1):354-61. [Link]
9. Al-Saadi HA, Al-Lami AA, Hassan FA, Al-Dulymi AA. Heavy metals in water, suspended particles, sediments and aquatic plants of Habbaniya Lake, Iraq. Int J Environ Stud. 2002;59(5):589-98. [Link] [DOI:10.1080/00207230212734]
10. Avinash V, Karne D, Prabhakar D. Studies on physico-chemical characteristics of freshwater bodies in Khatav Tahsil, Maharashtra. Nat Environ Pollut Technol. 2009;8(2):247-51. [Link]
11. Al-Kubaisi MH, Al-Heety EA, Yousif YM. Application of organic indicators and overall index to assess the level of water pollution in Habbaniya lake, Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2021;26:93-102. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.54.2A.7Ms-2021-07-28]
12. Hassan FM, Taylor WD, Al-Taee MM, Al-Fatlawi HJ. Phytoplankton composition of Euphrates River in Al-Hindiya barrage and Kifil city region of Iraq. J Environ Biol. 2010;31(3):343-50. [Link]
13. Salman JM, Hadi SJ, Mutaer AA. Spatial and temporal distribution of phytoplankton and some related physical and chemical properties in Al-Abasia river (Euphrates), Iraq. Int J Geol Earth Environ Sci. 2013;3(3):155-69. [Link]
14. Al-Zughaiby HH, Jawad HJ, Al-Awadi JH. The relationship between concentrations of some trace elements in the Euphrates River of Iraq. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020;2290(1):020044. [Link] [DOI:10.1063/5.0028128]
15. Al-Obaidy AHM, Al-Janabi ZZ, Shakir E. Assessment of water quality of Tigris River within Baghdad city. Mesop Environ J. 2015;1(3):90-8. [Link]
16. Asare-Donkor NK, Ofosu JO, Adimado AA. Hydro-chemical characteristics of surface water and ecological risk assessment of sediments from settlements within the Birim River in Ghana. Environ Syst Res. 2018;7(1):9. [Link] [DOI:10.1186/s40068-018-0113-1]
17. Al-Salihy AI, Soran NS, Al-Jumaily HA. Hydro-chemical evaluation of raw water and treated water in the liquefication plant of Kirkuk unified water project using WQI technique, Northern Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2021;54(1):78-87. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.54.1E.7Ms-2021-05-28]
18. Jiang Y, Gui H, Yu H, Wang M, Fang H, Wang C, et al. Hydro-chemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of rivers in different regions of cities: A case study of Suzhou city in northern Anhui Province, China. Water. 2020;12(4):950. [Link] [DOI:10.3390/w12040950]
19. Kannah AMA, Al-Jubouri MI, Aumary AW. Comparison between some water characters of the Lesser Zap with an impoundment ground water close to it. J Mosul Stud. 2018;1:212-22. [Link] [DOI:10.33899/rjs.2018.159363]
20. APHA. Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater. 16th ed. Washington DC: American Public Health Association; 2003. [Link]
21. Abbawi SA, Hassan MS. Practical engineering of the environment, water tests. Mosul: Dar Al-Hikma for printing and publishing; 1990. [Link]
22. Jassim SZ, Goff JC. Geology of Iraq. London: Distributed by GSL; 2006. [Link]
23. Al-Lami A. The environmental effects of the Tharthar arm on the Tigris river before entering the city of Baghdad: Baghdad Al-Mustansiriya University; 1998. [Link]
24. Awadh SM, Ahmed RM. Hydrochemistry and pollution probability of selected sites along the Euphrates River, western Iraq. Arab J Geosciences. 2013;6(7):2501-18. [Link] [DOI:10.1007/s12517-012-0538-1]
25. Fayyadh AM, Zaidan TA, Al-Heety EA. Evaluation of ground water quality in al-waffa and kubaysa areas using multivariate statistical analysis, Al-Anbar, Western Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2020;53(2):107-27. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.53.2D.8Ms-2020.10-30]
26. Fatah KK, Hamed M, Saeed MH, Dara R. Evaluation groundwater quality by using GIS and water quality index techniques for wells in Bardarash area, Northern Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2020;53:87-104. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.53.2c.7Rs-2020-09.07]
27. Al-Lami AA, Al-Jaberi HH. Heavy metals in water, suspended particles and sediment of the upper-mid region of Tigris River, Iraq. Proceedings of international symposium on environmental pollution control and waste management. 2002;4(12):97-102. [Link]
28. Serajuddin M, Chowdhury MA, Haque MM, Haque ME. Using turbidity to determine total suspended solids in an urban stream: A case study. 2nd International Conference on Water and Environmental Engineering (iCWEE2019); 2019 Jan; Dhaka. P. 19-22. [Link]
29. Al-Harahsheh ST, Al-Raggad M, Al-Shdaifat A, Al-Wreikat M. Hydrochemical evaluation of the azraq unconfined aquifer, Jordan. Iraq Geological J. 2020;53(2):1-18. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.53.2A.1Rw-2020-08-01]
30. ISDW No.417: Iraq Standards of Drinking Water. Iraqi Standards; 2009. [Link]
31. Khudair BH, Al-Musawi NO. Water quality assessment and total dissolved solids prediction using artificial neural network in Al-Hawizeh marsh, South of Iraq. J Eng. 2018;24(4):147-56. [Link]
32. Al-Janabi KWS, Alazawi FN, Mohammed MI, Khadum AAH, Mohamad AB. Chlorophenols in Tigris river and drinking water of Baghdad, Iraq. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011;87(2):106-16. [Link] [DOI:10.1007/s00128-011-0315-y]
33. Shivaramaiah HM, Sanchez-Bayo F, Al-Rifai J, Kennedy IR. The fate of endosulfan in water. J Environ Sci Health B. 2005;40(5):711-20. [Link] [DOI:10.1080/03601230500189311]
34. Douabul AA, Al-Saad HT, Abdullah DS, Salman NA. Designated protected Marsh within Mesopotamia: Water quality. Am J Water Resources. 2013;1(3):39-44. [Link]
35. Al-Dabbas MA, Kreamer DK, Al-Shammari AA, Jwad AM. Management of Bai Hassan unconfined aquifer, Lesser Zab River Basin, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2020;53(2B):1-23. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.53.2B.1Rs-2020-08-01]
36. Al-Kilabi JA. Hydrochemical comparison of groundwater in Dibdiba and Dammam Aquifers in the Karbala Plateau, Central Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2018;51(1):101-12. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.51.1.7Ms-2018-06-29]
37. Al-Kubaisi MH. Hydrochemical facies description to assess the water quality of Habbaniya Lake, Iraq. Iraq Geological J. 2020;53(2F):94-107. [Link] [DOI:10.46717/igj.53.2F.7Ms-2020-12-30]
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |







